Project Management Life Cycle Phases - Shikshaglobe
What is a Project Management Life Cycle?
Project Management Life Cycle is a progression of fundamental exercises for achieving project goals or targets. A system incorporates the stages to change a thought into the real world. Undertakings might have various aspects and trouble levels, yet they can be planned to the Project Management life cycle structure, anything that the venture's size is.
Project Management Life Cycle Phases
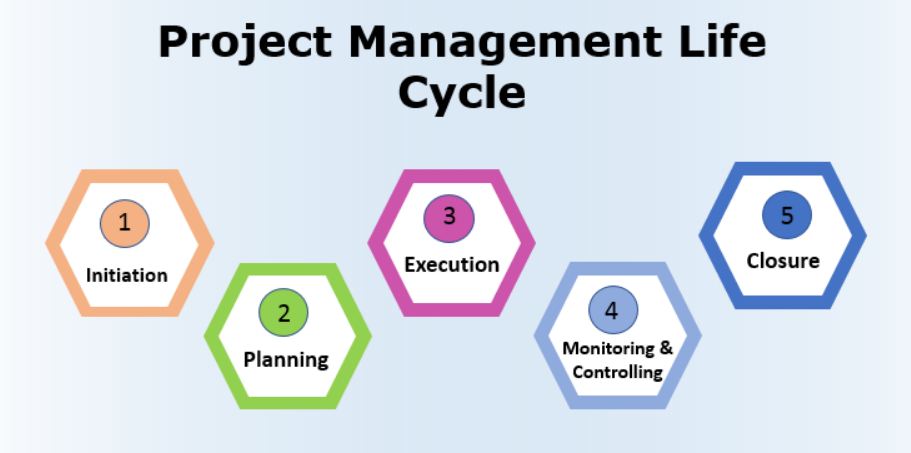
The Project Management Lifecycle process is partitioned into four fundamental parts: Initiation stage, Planning stage, Execution stage, and Monitoring, Controlling, and Closing stage as displayed in the underneath chart.
We will look at each Project's Life Cycle phase:
Project Initiation Stage
The inception stage characterizes those cycles that are expected to begin another task. The reason for the undertaking commencement stage is to figure out what the task ought to achieve.
This stage mostly made out of two fundamental exercises
Foster a Project Charter and
Recognize Stakeholders
All the data connected with the undertaking are placed in the Project Charter and Stakeholder Register. At the point when the task contract is supported, the venture turns out to be authoritatively approved.
Project Charter
The Project Charter characterizes the undertaking's principal components
Experience the difference
Project objectives
Project limitations and Problem explanations
Allocate project director
Partner list
Significant level timetable and financial plan
Achievements
Endorsements
This record permits a task chief to use hierarchical assets for the undertaking. To make a task sanction, the sources of info required will be venture climate factor, business case, arrangements, an undertaking explanation of work and hierarchical cycle resources.
NTT Admission
Distinguishing Stakeholders
A partner can impact the achievement and disappointment of the task. To note down the data about the partner, a Stakeholder Register is utilized.
The partner register will have data like
Kind of partner
Assumption for partner
Job in Project ( Business Analyst, Tech engineer, Client PM)
Assignment (Director, Business Lead, and so forth.)
Type Communication ( Weekly/Monthly)
Impact on the undertaking ( Partial/Supportive/Influensive)
Different exercises associated with starting cycle bunch are:
Take the next step>>>
Appointing the undertaking director
Deciding on the partner's needs, assumptions, and undeniable level of necessities
Characterize the undertaking a positive outcome measures
Recognize specific spending plans for a specific stage
Ensure that the undertaking is lined up with the association's key objective
The partner register and task sanction are utilized as contributions to the next advancement gatherings, for example, arranging process bunch.
See also here -->>
NTT Admission
Project Planning Stage
Project Planning stage covers around half of the entire cycle. Arranging stage decides the extent of the task as well as the goal of the venture. It starts with the results of inception stage (contract, fundamental extension proclamation, and task director). The result of the arranging stage fills in as the contribution for the execution stage.
The project management life cycle consists of distinct
phases that guide the progression of a project from initiation to closure. Each
phase serves a unique purpose and involves specific tasks, deliverables, and
stakeholders. Here are the typical phases of a project management life cycle:
1. Initiation
Phase:
·
Purpose: In this phase, the project's
feasibility and alignment with organizational goals are assessed. The project's
objectives are defined, and initial planning begins.
·
Key Activities:
·
Project charter creation.
·
Stakeholder identification.
·
High-level scope definition.
·
Initial risk assessment.
·
Deliverables: Project charter, initial
scope statement, stakeholder register.
2. Planning
Phase:
·
Purpose: Detailed planning takes place in
this phase, covering scope, schedule, resources, and budget. The project plan
is created to guide the execution phase.
·
Key Activities:
·
Detailed scope definition.
·
Work breakdown structure (WBS) development.
·
Activity sequencing and duration estimation.
·
Resource allocation.
·
Cost estimation and budgeting.
·
Risk management plan.
·
Deliverables: Project management plan,
WBS, schedule, budget, risk management plan.
3. Execution
Phase:
·
Purpose: This phase involves carrying out
the project work according to the project plan. Team members perform tasks, and
project progress is monitored.
·
Key Activities:
·
Task execution.
·
Team management.
·
Quality assurance.
·
Communication and reporting.
·
Risk monitoring and control.
·
Deliverables: Completed project work
packages, progress reports.
4. Monitoring
and Controlling Phase:
·
Purpose: Continuous monitoring of project
performance occurs in this phase. Deviations from the plan are identified and
corrective actions are taken.
·
Key Activities:
·
Performance measurement.
·
Issue identification and resolution.
·
Change control.
·
Quality control.
·
Risk management updates.
Music Teacher Training Course Admission
·
Deliverables: Change requests, updated
project management plan, performance reports.
5. Closing
Phase:
·
Purpose: The project is formally closed
in this phase. All project activities are completed, and the final deliverables
are handed over to the client or stakeholders.
·
Key Activities:
·
Final inspection and verification.
·
Documentation completion.
·
Stakeholder acceptance.
·
Project closure report.
·
Lessons learned documentation.
·
Deliverables: Project closure report,
lessons learned, formal acceptance, handover documents.
6. Post-Implementation
Review (Optional):
·
Purpose: While not always considered a
formal phase, a post-implementation review occurs after project closure to
assess the project's success, capture lessons learned, and evaluate the
achieved benefits.
·
Key Activities:
·
Evaluation of project performance.
·
Benefits realization assessment.
·
Documentation of lessons learned.
·
Stakeholder feedback.
· Deliverables: Post-implementation review report, updated organizational knowledge base.
The significant parts of arranging process are
Arranging stage ought not be executed before your underlying arranging is done
Until the execution interaction doesn't begin, you shouldn't quit overhauling plans
Make Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
For any effective task WBS (Work Breakdown Structure) is significant. Following are moves toward make WBS.
Lead a talk to list every one of the errands
Include your entire group for conceptualizing
Record the design tree of the errand otherwise called WBS (work breakdown structure)
Further breakdown your top WBS into a various leveled set of exercises, for example, classes, sub-classifications, and so on. For instance equipment, programming, student, supervisory groups, and so on.
Characterize how to record the things into your WBS
Ask others - it tends to be a specialist, experienced work force, and so on.
Granularity-how nitty gritty your errand would it be advisable for you to have? Assessing cost and time for higher granularity is hard while for lower granularity it will be hindered with too definite data
Granularity ought to be of right level not excessively high or not excessively low
Arranging Schedule Management
Plan Scheduling is the method involved with laying out the technique, arrangements and documentation for arranging, making due, executing and controlling the task plan. The contributions to these exercises incorporate
Project the executive's plan
Project Charter
Endeavor natural elements
Authoritative interaction resources
The result of the Planning Schedule Management incorporates
Plan the board plan
Characterizing Activities
Characterizing Activities is the strategy for recording and recognizing explicit activities to be performed to create the venture expectations.
Project Management Life Cycle: Complete Guide
In characterize exercises, each work bundles is separated into individual plan for getting work done exercises. The contributions of the characterizing exercises incorporate
Plan the executives plan
Scope benchmark
Venture natural elements
Hierarchical interaction resources
While the results of these exercises are
Movement list
Movement ascribes
Achievement list
Grouping Activities
Grouping exercises is only coherently sorting out the result of "characterize exercises". It decides the request where the exercises should be performed.
Project Management Life Cycle: Complete Guide
The principal yield from the grouping action process is the "Organization Diagram".
Network outline is only posting the errand on a board in a coherent request.
For instance, if you need to begin a business outside the country what will be your rundown of exercises, and what will be the request it ought to be finished?
You will perform exercises in these request
Pick a country
Get license to operate
Employing a supervisor
Purchasing a property
Purchasing the furniture and so on.
Starting the business
Assessing Activity Resources
This stage makes sense of the method involved with assessing the work exertion and assets expected to finish the job. The other element that must be considered at this stage is the accessibility of the assets.
While assessing assets, the attention ought to be on the longest way of the arrangement (Critical Path), which going to consume additional time and cash.
You need to gauge assets for two undertakings
Basic errands
Drifting errands
Ensure that your basic errands are precisely assessed (consummation time).
There are five sources of info used to assess movement assets
Plan Management Plan
Action list
Asset Calendar
Undertaking natural elements
Authoritative interaction resources
The result of this stage is
Action asset necessities
Asset breakdown structure
Project records refreshes
NOTE: All the action that is done as such far (characterize exercises + grouping exercises + Estimate action assets) will help in "Foster Schedule."
Assessing Activity Durations
Assessing Activity Duration is the most common way of assessing the quantity of work time frames (weeks/months) expected to finish the singular responsibility with assessed assets. This step characterizes what amount of time a singular errand will require to finish.
You can't ascertain action length without computing the work exertion and assets expected to finish the job. Assessing cycle ought to be finished in a specific order
Gauge work exertion first
Followed by assessing the assets
Followed by Estimating the term of assignment
To gauge action lengths, you really want inputs
Action list
Action credits
Asset schedules
Project scope articulation
Hierarchical interaction resources
Endeavor natural elements
While there are two primary results
Gauge action spans
Gauge action spans project record refreshes
This procedure likewise alludes as PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Techniques) gauges.
Foster Schedule
Foster Schedule is the method involved with dissecting action successions, asset prerequisites, terms and timetable imperatives to make the venture plan model. For booking each undertaking, three fundamental elements are thought about
Length
Task conditions
Requirements
Utilizing these variables project works out the beginning date and finish date for each assignment.
A planning program can be utilized to make a timetable. It produces a timetable model with arranged dates for finishing project exercises.
The contribution of this apparatus incorporates
Plan the board plan
Movement list
Movement ascribes
Project plan - network graphs
Action asset necessities
Asset schedules
Action length gauges
Project scope articulation
Risk register
Project staff tasks
Asset breakdown structure
Undertaking natural variables
Authoritative cycle resources
The result from this would be
Project Schedule
Project network graph
Gantt diagrams or Bar outlines
Achievement diagram
Plan gauge
Booked information
Project report refreshes
Control Schedule
The last phase of the arranging stage is Control Schedule. It is the method involved with observing the situation with project exercises to refresh the project process and oversee changes to the timetable benchmark.
Assuming changes are expected to the timetable, they should go through the change control process. The timetable ought to be overseen or constrained by the director proactively.
There are four principal results of the control plan process
Project the executive's plan
Plan benchmark
Plan the board plan
Project plan
Work execution data
Authoritative cycle resources
There are five results of the control plan
Work execution of the board
Authoritative cycle resources refreshes
Change demand
Project the executives plan refreshes
Project archive refreshes
Project Execution Stage
The executing stage comprises those exercises that are characterized in the project by the executive's plan. This cycle includes overseeing partner assumptions, planning with individuals and assets, too











