All About Client Copy – Local,Remote, Import/Export - Shikshaglobe
Client Copy
We can produce a clear client with SCC4.But how to fill the information in the client? "Answer is the client duplicate."
Client duplicate signifies "moving client explicit information" inside a similar instance(SID) or between various instances(SID).
Client duplicate can be performed with three unique strategies -
Nearby client duplicate.
Distant client duplicate.
Client Import/Export.
Beneath brief subtleties are given about client duplicate techniques.
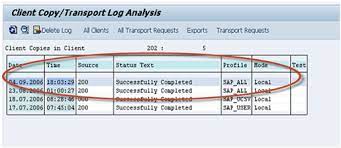
Neighborhood Client Copy: - This strategy is utilized to duplicate client inside a similar example (SID).It is finished by T-code SCCL.
SAP Client Copy: Local, Remote, Import/Export
Far off Client Copy: - This strategy is utilized to duplicate client between various instances(SID).It is performed by T-code SCC9.
We can produce a clear client with SCC4.But how to fill the information in the client? "Answer is the client duplicate."
Client duplicate signifies "moving client explicit information" inside a similar instance(SID) or between various instances(SID).
Client duplicate can be performed with three unique strategies -
Neighborhood client duplicate.
Far off client duplicate.
Client Import/Export.All About SAP Client Copy – Local, Remote, Import/Export
In SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data
Processing), client copies are essential processes that involve duplicating
data, configurations, and settings from one client to another within the same
SAP system or between different SAP systems. This helps organizations manage
and maintain various SAP environments efficiently. Let's explore the different
types of SAP client copies - Local, Remote, Import, and Export:
1. Local Client Copy:
A local client copy refers to the process of copying data, configurations, and settings from one client to another within the same SAP system. It is typically used for activities like creating sandbox or test clients, refreshing clients, or splitting clients.
Nursery and Primary Teachers Training Course Admission
Key Points:
- Within
the Same System: Local client copies occur within the boundaries of a
single SAP system.
- Data
Subset: You can choose to copy all client data or a subset of it, such
as customizing data or application data.
- Change
Logs: Local client copies can be executed with or without change logs.
2. Remote Client Copy:
Remote client copy involves copying data, configurations,
and settings from one SAP system to another. This is useful for scenarios like
setting up a new system with the same data and configurations as an existing
one or consolidating data from multiple systems.
Key Points:
- Between
Different Systems: Remote client copies occur between separate SAP
systems.
- Transport:
Transport mechanisms, such as SAP transport requests, are typically used
to move the client data from one system to another.
- Data
Subset: Similar to local copies, you can choose to copy all data or a
subset.
3. Client Import:
Client import is the process of importing a client's data,
configurations, and settings into an existing SAP system. It is often used when
you want to set up a new client in an existing system using data and configurations
from another system.
Keep reading |
Key Points:
- New
Client Creation: Client import is commonly used when creating a new
client within the same SAP system.
- Data
Transfer: The client's data is transferred into the target system
using import methods.
- Transport
Mechanism: Transport requests are often used to move the data.
4. Client Export:
Client export involves exporting data, configurations, and
settings from an existing SAP client, typically for the purpose of transferring
it to another SAP system or for backup purposes.
Key Points:
- Data
Extraction: The data is extracted from the source client, and export
methods are used to create export files.
- Backup
and Recovery: Client exports are often used for creating backups of
client data for disaster recovery.
- Transport:
Transport mechanisms, like transport requests, are used for moving the
export files to other systems.
Common Considerations:
- Authorizations:
Adequate authorizations are required to execute client copies, especially
remote client copies, as they involve data transfer between systems.
- Data
Selection: Depending on your requirements, you can choose to copy all
data or select specific data subsets, such as customizing data,
application data, or user data.
- System
Landscape: Understanding your SAP system landscape is crucial, as it
dictates whether you'll be performing local or remote client copies and
whether you need import or export processes.
- Transport
Mechanisms: SAP transport mechanisms are commonly used for remote
client copies and client import/export processes, ensuring data integrity
and consistency.
Click here for details
Beneath brief subtleties are given about client duplicate strategies.
Neighborhood Client Copy: - This strategy is utilized to duplicate client inside a similar occasion (SID).It is finished by T-code SCCL.
SAP Client Copy: Local, Remote, Import/Export
Distant Client Copy: - This strategy is utilized to duplicate client between various instances(SID).It is performed by T-code SCC9.
For a neighborhood duplicate, the framework should have sufficient room in the data set or tablespace.
For remote duplicate, target framework should have sufficient room in the data set or tablespace. Check space utilizing Tx DB02.
To stay away from irregularities during client duplicate clients ought not be permitted to work in source client.
rdisp/max_wprun_time boundary ought to be changed to 2000 second as a SAP suggestion . Despite the fact that you utilize equal cycles and timetable work behind the scenes, discourse cycles will be utilized.
Neighborhood Client Copy
Nearby client duplicate is performed utilizing Tcode SCCL.
Situation:-
Source Instance and client := DKM-000
Target Instance and client := DKM-202
Create a passage for your new objective client utilizing SCC4. In our situation, we will make client 202 in DKM system.Log on to this recently made target client (DKM-202) with client SAP* and default secret phrase pass.
Excute T-code SCCL.
By default Client Copy is executed as a solitary cycle. A Single cycle will take a ton of time. We will convey the responsibility of single the cycle to parallel(multiple) processes which will lessen time in replicating a client.
Select Goto from the menubar.
Select Parallel Process.Parallel processes are utilized to take advantage of the limit of data set better
| Your gateway to success |
How to trade client?
Log on to the objective system(DKM). Make a passage for your new objective client utilizing SCC4. Sign on to the source framework/source client(PKT).Before you import a Client you want to export.Export is only moving information records and co-documents from source framework's data set to focus on framework's import buffer.Execute T-code SCC8.Once the occupation is executed information documents and co-records of profiles from PKT framework's data set are moved to DKM framework's import buffer.Once we will import demand in DKM really at that time it will be reflected in a data set of DKM framework.Contingent upon the picked trade profile there can ultimately depend on 3 vehicle demands made:
Demand PKTKO00151 will hold the cross-client information,
Demand PKTKT00151 will hold the client subordinate information,
Demand PKTKX00151 will likewise hold some client subordinate information.
How to import the client?
Log on to the recently made target client(DKM-202) utilizing SAP* and secret word pass.
Start the STMS_IMPORT exchange
See also here -->>
Must Know!
| SAP Kernel Updates |
| All About Client Copy – Local,Remote, Import/Export |
| Introduction to Transport Management System (TMS) |
| How to configure TMS (Transport Management System) |











